Role: Researcher
NbC precipitation in Ferrite.
The aviation industry is often seeking methods to improve the efficiency of materials under extreme conditions. Precipitation is the aggregation of impurities in certain materials, to form nodule-like formations (the precipitates) that affect the properties of the material. In certain cases, they can improve the resistance to fatigue (so that they break down at higher temperature and higher stresses).
Role: research associate, honorary researcher
Dynamics of influenza viruses.
Predicting how strong the next influenza season will be and when it will peak has been a target of research activity for its implications in the managment of public health facilities, and for a more general understanding of the mechanisms underlying its transmission.

Role: research fellow
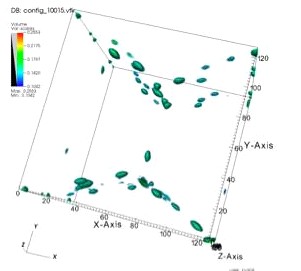
Solidification of binary eutectic alloys.
Eutectic composites are common microstructures arising during the solidification process of various metal alloys. They form domains of distinct composition that interconnect, affecting the properties of the resulting material. Metallurgists seek to understand what patterns, and thus what properties, result from the specific conditions under which these alloys solidify. Physicists are interested on the more general aspect of pattern forming systems.

Role: research associate, invited professor
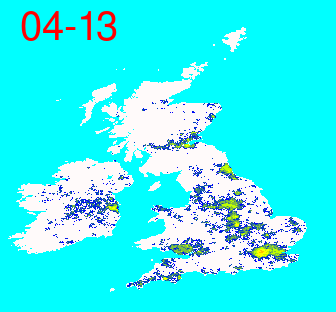
Dynamics of infectious diseases.
The spread of an infectious disease results from the combined effects of short contact transmission, long-distance transport, demography, social interactions, environmental conditions, and the characteristic of the infective agent itself. These mechanisms operate on very different spatial and temporal scales. The ability to cross these scales permits to peek into the mechanisms that underline the spread of a disease in areas with different population characteristics.
Role: Founder and developer
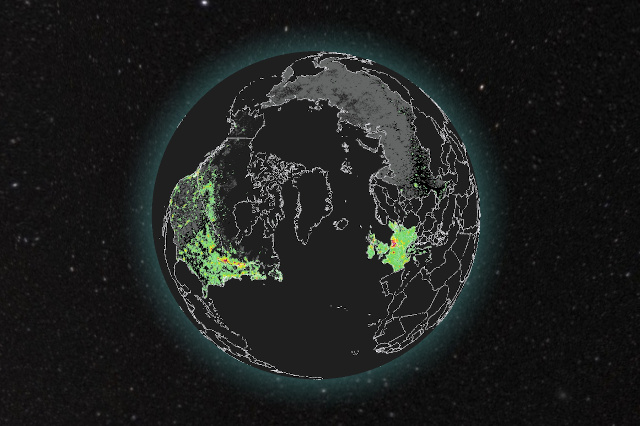
Forecasting infectious diseases.
The company was founded with a simple mission: to harness the power of data and modelling to provide clear, location-specific forecasts for infectious diseases usable by everyone. Forecasts are designed to empower everyone, but they hold particular value for those facing heightened risks: people with health conditions, caregivers, or anyone wanting to make informed decisions.
Role: Marie-Curie fellow
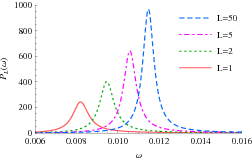
Stochastic effects in infectious disease
Whenever a systems is made up of many components, it is quite natural to talk about average values. When the number of components of the system is small, however, these quantities are subjected to large fluctuations. In epidemiology, with local populations composed of a relatively low number of individuals, this can cause huge stochastic fluctuations in the dynamics of infections that, in some cases, may explain the multi-annual recurrence of certain diseases.
Role: research associate
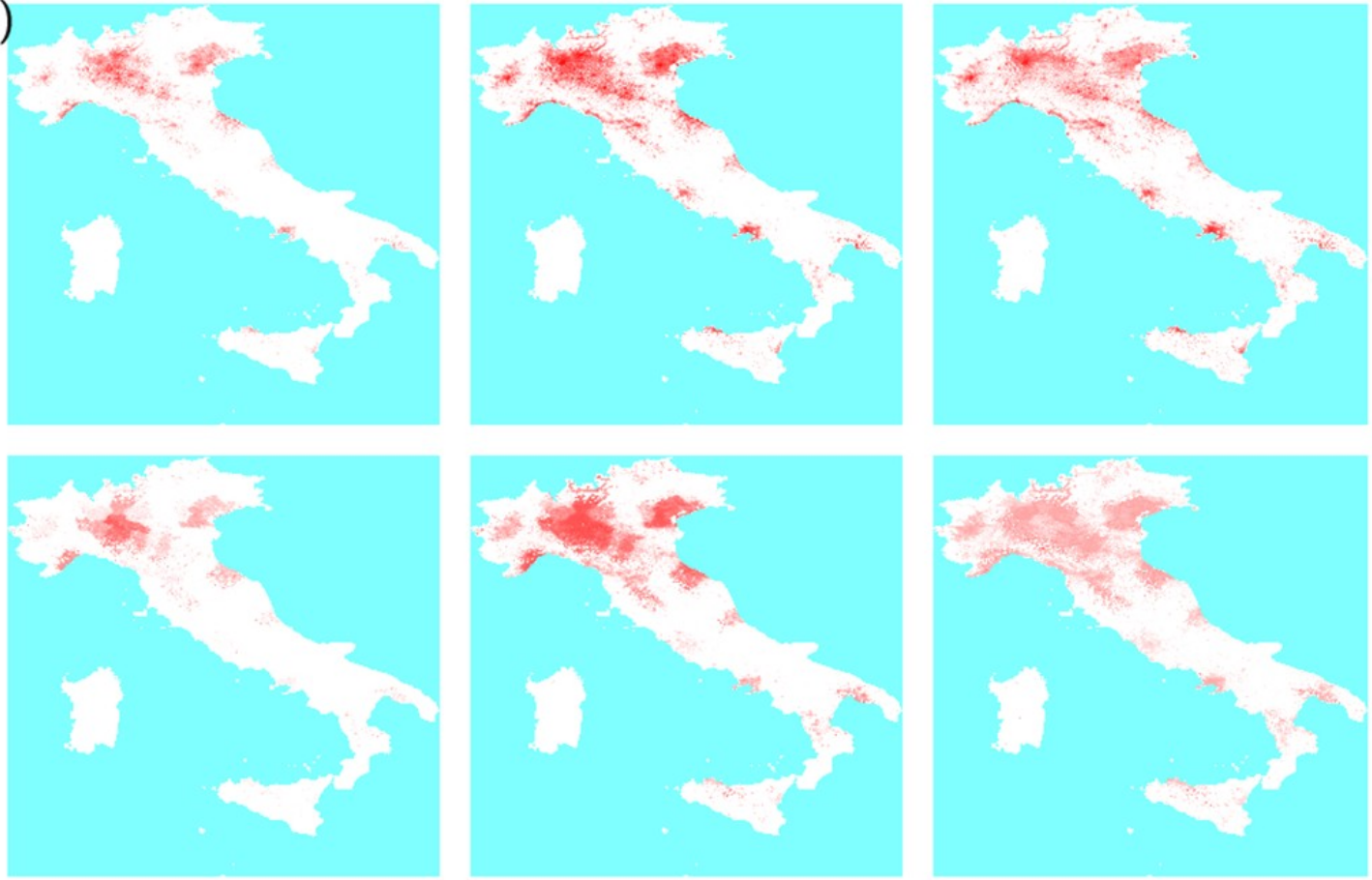
COVID-19 circulation
With an estimated potential of 30 million deaths worldwide, the COVID19 pandemic was one of the major threat to public health since the 1918 flu pandemic. Worldwide response contained the spread of the virus until vaccines became available. Understanding the effects of governmental intervention has been a fundamental goal of epidemic modelling during the pandemic years.

Logos shown on this page are used in accordance with their respective licences:
- École polytechnique, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
- Universidade de Lisboa, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons